YUGA
YUGA Introduction
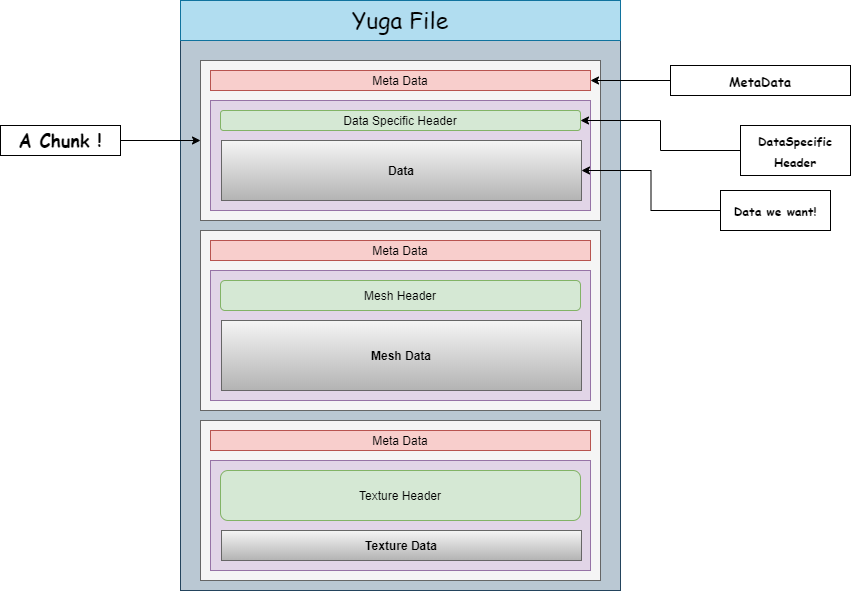
YUGA files are files that contain multiple resources inside them such as Meshes, Textures and Shaders that we call chunks.
Asset Type
enum class AssetType : uint8_t {
Unknown = 0,
Description = 1,
Mesh = 2,
Texture = 3,
RawFile = 4,
Shader = 5,
Material = 6,
AssetList = 7,
.
.
.
}Meta Data and Chunk Header
Each Resource in a YUGA File has a Meta Data that comes before them in memory.
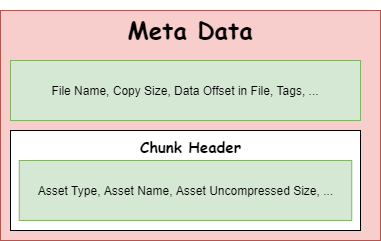
Data such as:
- Size of meta data
- Offset of header in file
- File name
- Chunk Header
- Size of the data that comes after
- Whether it’s compressed or not
- Revision number.
Meta Data in our header file:
MetaData Struct
struct Metadata {
bool valid = false;
bool is_remote = false;
uint16_t number_in_file = 0;
uint32_t copy_size = 0; // If you want a copy of the chunk meta data (i.e. everything,) this is the total size
uint64_t offset_of_header_in_file = 0;
uint64_t offset_of_asset_in_file = 0;
ChunkHeader chunk_header;
char reserved [6] = {};
uint16_t file_name_size = 0;
char const * file_name = nullptr; // Nul-terminated, but size (plus the nul) is in file_name_size.
char const * asset_name = nullptr; // size (including the NUL) is in the header. If that is zero, then this will be nullptr.
char const ** tag_names = nullptr; // array of nul-terminated strings, count is in the header. If that is zero, then this will be nullptr.
char const ** tag_values = nullptr; // ditto
};Chunk Header in our header file:
ChunkHeader Struct
struct ChunkHeader {
uint8_t signature [4] = {'Y','U','G','A'}; // 0
uint64_t skip_bytes = 0; // 4
ChunkFlags chunk_flags = ChunkFlags::None; // 12
AssetType asset_type = AssetType::Unknown; // 13
uint16_t asset_name_size = 0; // 14 // Includes the NUL
uint16_t asset_revision = 0; // 16
uint16_t asset_tags_size = 0; // 18 // Includes the NUL
uint16_t asset_tags_count = 0; // 20
uint16_t reserved = 0; // 22
uint32_t asset_uncompressed_size = 0; // 24
uint32_t asset_uncompressed_hash = 0; // 28 // Doesn't cover chunk header or name or tags; only content (i.e. the asset.)
// 32
};
How We Write Assets
We write the assets using a FileWriter Class.
File Writer Interface
class FileWriter {
bool ok () const {return m_out.ok();}
bool in_chunk () const {return m_chunk_state.in_chunk;}
bool in_tags () const {return m_chunk_state.in_tags;}
// For LZ4, 0 is the default (low-medium compression, really fast)
// 1..16 are the HC algorithm, the higher the better and slower compression
// -1..-16 are the accelerated algorithm, with lousy compression but even faster speed
void set_compression_hint (int level) {m_comp_state.hint = level;}
bool chunk_start (AssetType asset_type, CBlob const & asset_name, uint16_t asset_rev, ChunkFlags should_compress = ChunkFlags::Compressed);
bool chunk_start (AssetType asset_type, char const * asset_name, uint16_t asset_rev, ChunkFlags should_compress = ChunkFlags::Compressed);
bool chunk_emit_tag (CBlob const & name, CBlob const & value = {});
bool chunk_emit_tag (char const * name, char const * value = nullptr);
bool chunk_end_tags ();
bool chunk_emit_data (CBlob const & data);
ChunkFinishResult chunk_finish ();
bool chunk_emit_data_texture_start (TextureHeader const & texture_header);
bool chunk_emit_data_texture_data (CBlob const & data);
};writer.chunk_start(YUGA::AssetType::Shader, asset_name, (uint16_t)asset_revision, YUGA::ChunkFlags::Compressed);
writer.chunk_emit_tag("source_file_name", std::filesystem::path(input_path).filename().string().c_str());
writer.chunk_emit_data(CBlobAliasOf(header));
writer.chunk_emit_data({ blocks.data(), blocks.size() * sizeof(YUGA::ShaderDataBlock) });
writer.chunk_emit_data({ variables.data(), variables.size() * sizeof(YUGA::ShaderDataVariable) });
writer.chunk_emit_data(compiler_result.spirv);
writer.chunk_emit_data({ defines.data(), defines.size() * sizeof(YUGA::ShaderDefine) });
writer.chunk_emit_data({ string_table.data(), string_table.size() });
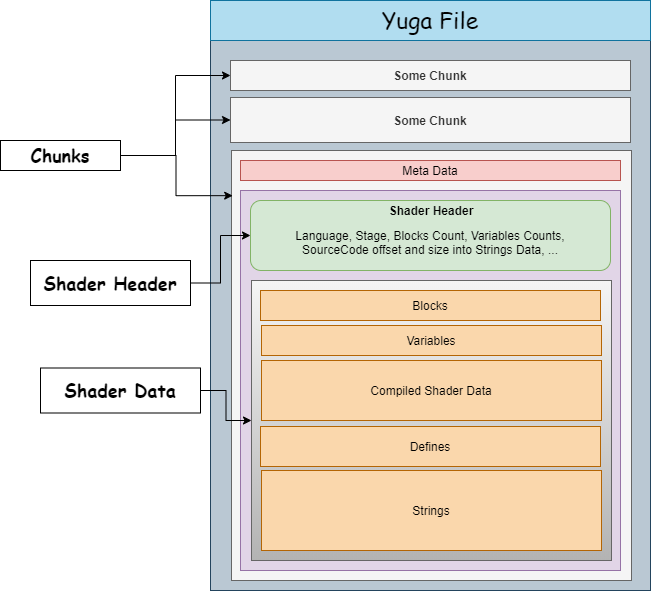
Shader Header
struct ShaderHeader {
uint64_t key;
ShaderStage stage;
ShaderLanguage language;
ShaderIrFormat ir_format;
uint8_t entry_point_params_count;
uint32_t entry_point_name_str_offset;
uint32_t source_str_offset;
uint32_t ir_bytes;
uint32_t string_table_bytes;
uint16_t entry_point_name_str_bytes;
uint16_t source_str_bytes;
uint16_t blocks_count;
uint16_t variables_count;
uint16_t defines_count;
char reserved[2];
}class Shader : public GenericAsset {
public:
explicit Shader (Metadata const * meta_data, Blob const & asset_mem);
public:
ShaderHeader const & header() const {return *reinterpret_cast<ShaderHeader const *>(asset());}
size_t header_size() const {return sizeof(ShaderHeader);}
Byte const * data () const {return asset() + header_size();}
size_t data_size () const {return asset_size() - header_size();}
CBlob blocks() const {return {data() + header().blocks_offset(), header().blocks_bytes()};}
CBlob variables() const {return {data() + header().variables_offset(), header().variables_bytes()};}
CBlob ir() const {return {data() + header().ir_offset(), header().ir_bytes};}
CBlob defines() const {return {data() + header().defines_offset(), header().defines_bytes()};}
CBlob strings() const {return { data() + header().string_table_offset(), header().string_table_bytes};}
ShaderDataBlock const * block(uint32_t index) const {
YUGEN_ASSERT(index < header().blocks_count);
return blocks().as<ShaderDataBlock const>() + index;
}
ShaderDataVariable const * variable(uint32_t index) const {
YUGEN_ASSERT(index < header().variables_count);
return variables().as<ShaderDataVariable const>() + index;
}
ShaderDefine const * define(uint32_t index) const {
YUGEN_ASSERT(index < header().defines_count);
return defines().as<ShaderDefine const>() + index;
}
char const * block_name(ShaderDataBlock const * block) const {
return string(block->name_str_offset);
}
char const * block_name(uint32_t index) const {
return string(block(index)->name_str_offset);
}
char const * variable_name(ShaderDataBlock const * variable) const {
return string(variable->name_str_offset);
}
char const * variable_name(uint32_t index) const {
return string(variable(index)->name_str_offset);
}
char const * define_name(uint32_t index) const {
return string(define(index)->name_str_offset);
}
char const * define_value(uint32_t index) const {
return string(define(index)->value_str_offset);
}
char const * string(uint32_t offset) const {
YUGEN_ASSERT(offset < header().string_table_bytes);
return strings().as<char const>() + offset;
}
char const * entry_point_name() const {return string(header().entry_point_name_str_offset);}
char const * source() const {return string(header().source_str_offset);}
};